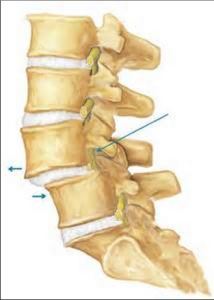
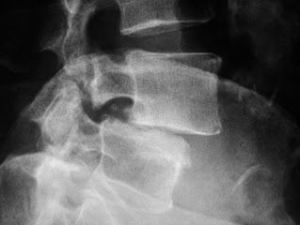
Spondylolithesis refers to incorrect stacking of the spinal vertebra on top of each other. It may also refer to mild or moderate instability of the spine. This incorrect stacking creates a “step off” of the vertebra seen on X-Ray. Normally, the bones stack up nicely on top of each other. Most likely due a genetic weakness of the ligaments supporting the spine (or trauma), one vertebra of the back-slides off of another. This may result in bony degeneration/arthritis, and/or impact on the nerve roots as they leave the spine, producing sciatica.
The pain with spondylolithesis is usually dull and constant, and is worse with spinal flexion and twisting. Not only may sciatica-type pain ensue, but symptoms like those of spinal stenosis are sometimes seen. Conventional treatment includes monitoring and physical therapy. More severe cases may require surgery for stabilization.